Celestial navigation
science, art and seafaring tradition
How to calculate altitude and azimuth using a free and intuitive spreadsheet (excel)

....after having collected all the data : estimated latitude and longitude, declination / local hour angle of the observed celestial bodies (stars, sun, moon and planets ) and sextant reading (altitude) ... we must calculate at least four data. We’ll use these to plot lines of position (LOP) on a nautical chart, plotting work sheet, or a simple graph paper to determine the position of the ship.
The data we need are : true altitude, LHA/declination, computed (estimated) altitude and azimuth
We can use this simple excel file to verify (or avoid) the manual calculations !
The file consists of four worksheet.
To prevent damages in cells containing formulae the worksheets are protected and cells are locked, we may use the unlocked cells only (green background).
When we open Excel, Excel automatically selects “Corrections to a sextant obser. “. for us. (The name of the worksheet appears on its sheet tab at the bottom of our document window.)
Example
On January 17th 2016 a Deck Officer takes and records the following sight :
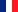
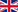
- Sun ( lower limb ) - sextant altitude 29° 53,5’ at 12h 23m 45s U.T.
- DR position : Latitude 38°34,2’ North – Longitude 005°32,7’ East
- Height of eye above the sea level : 2,5 meters
- Sextant is affected by errors. Corrections: +0,5’ instrument error (eccentricity) and -1,4’ index error
First of all we convert the sextant altitude to observed altitude using “Corrections to a sextant obser. “ worksheet :
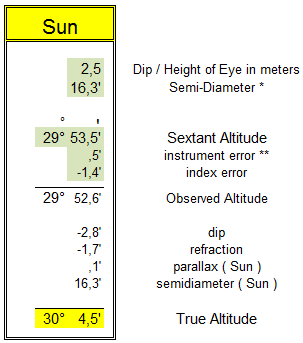
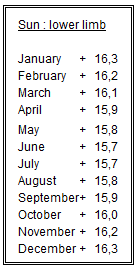
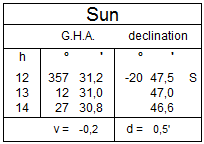
From the Nautical Almanac – January 17th 2016 :
at 12.00 U.T. :
- GHA 357° 31,2 v correction : -0,2’
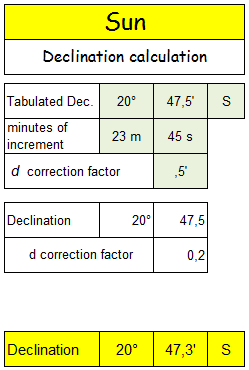
- Declination 20° 47,5’ S d correction : 0,5’
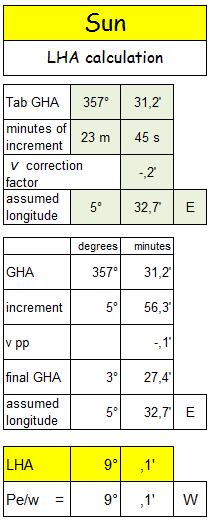
We calculate LHA and declination using “LHA – declination “ worksheet :
 |
We solve the formulae of celestial navigation calculating computed (estimated) Altitude and Azimuth using “Altitude - Azimuth“ worksheet :
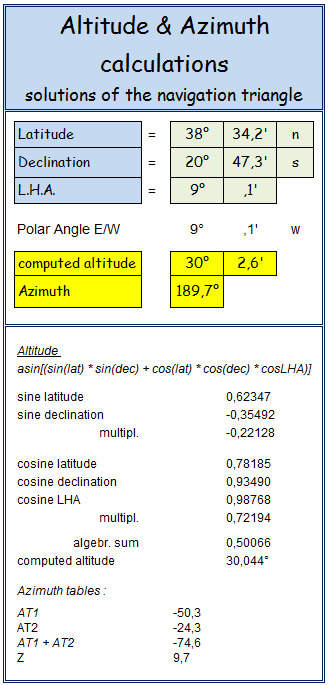
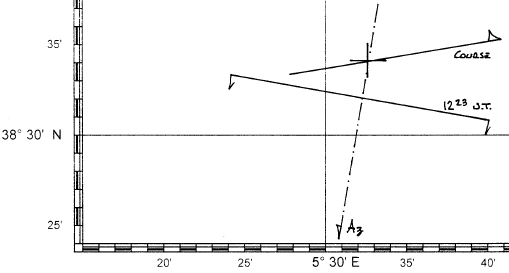
Difference of altitude = true altitude – computed altitude: 30° 04,5’ – 30° 02,6’ = + 1,9’
Now we can draw the graph:
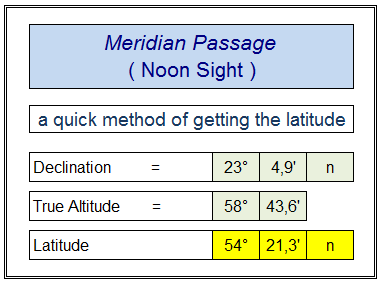
The last worksheet is named “ meridian altitude “. It allows to obtain the latitude after having insertered the meridian altitude and declination.
example:
We have a true altitude at meridian passage of 58° 43,6’ and a declination of 23° 04,9’ N : the latitude is 54° 23,3’ North.
| download |
celestial navigation - nautical astronomy formulas
formula altitude: sine altitude = (sine latitude * sine declination) + (cos latitude * cos decl * cos polar angle)
formula azimuth: cotg azimuth = ( cotg ( 90-declination) * cos latitude * cosec polar angle ) - (sine latitude * cotg polar angle )
| Exercises book |
© 2006-2024 www.nauticalalmanac.it